One of India’s busiest and fastest-growing states in terms of textile, apparel, and technical textile production as well as defense industry is Uttar Pradesh. Numerous projects, Memorandums of Understanding, and industrial development have resulted from the combination of favorable policies, a sizable labor force, infrastructure investments, strategic corridors, and backing from the federal and state governments (Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat).
The UP defense industrial corridor (nodes, investment, MSMEs, etc.) and the textile industry (growth, policy, projects) are covered in turn below, along with the overlaps (e.g. defense textiles, ballistic materials). I also discuss the keywords you mentioned in detail.
1. Foundations: Textile Strength & Policy Support
Growth of the UP Textile Industry
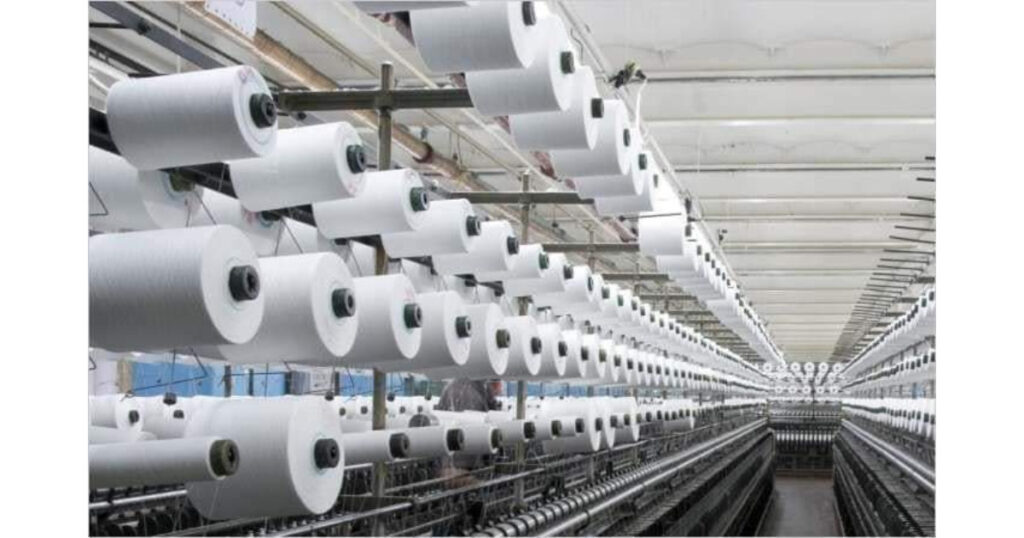
From the silk weaving in Varanasi to the handloom clusters in Bhadohi and the Chikankari skill in Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh has long been a center of textile traditions. The size and variety have developed into industrial power. Better infrastructure, investments, and an emphasis on exports have all contributed to the UP textile industry’s recent economic acceleration.
Handloom powerloom clusters in UP Bhadohi and Lucknow are still essential. Powerloom activity is high in Bhadohi, which is well-known for its carpets and rugs, and the surrounding districts. Lucknow supplies artisanal high-value output with its handloom base and elaborate Chikankari embroidery.
However, via new investments, support for innovative textiles, and worldwide integration, traditional strength is increasingly blending with contemporary goals.
The 2022 UP Textiles Policy
The UP textiles strategy 2022, which outlines incentives, subsidies, and support systems meant to stimulate both traditional and modern textile industry, is a crucial enabler. Important elements consist of:
- 25% capital subsidy for plant and machinery, plus further incentives for establishing in underdeveloped areas (Poorvanchal, Bundelkhand).
- Infrastructure subsidy: A portion of the money spent on building roads, drainage systems, water supplies, and electricity in industrial settings.
- Power and electricity incentives include a ten-year exemption from electricity duty for new textile or apparel units and a tariff subsidy for units located in PM MITRA parks.
- Freight reimbursement: Over a five-year period, 75%, 50%, and 25% of container freight costs will be reimbursed in order to increase exports.
- Support for the silk industry includes grants for sericulture, spinning, and reeling, particularly for businesses that use local koyas to produce silk thread.
UP Industrial Growth wants to transform its textile industry from artisanal and regional to globally competitive by coordinating policy assistance with industrial ambition.
2. Scaling Up: PM MITRA Parks & Technical Clusters
PM MITRA Parks Up

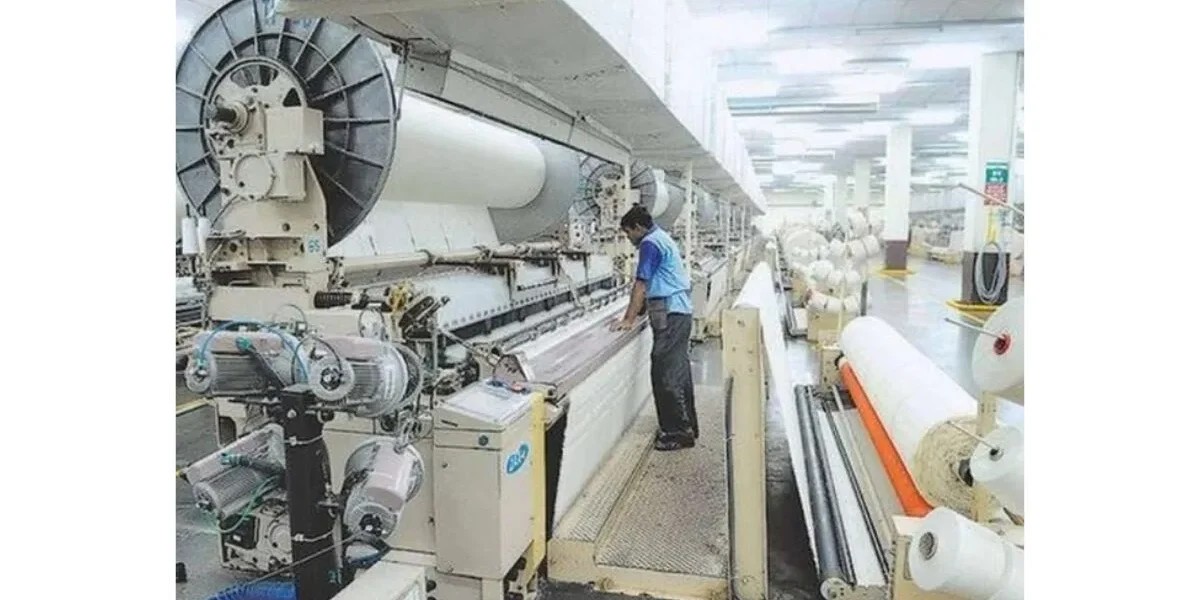
The PM MITRA parks UP program is one of the primary tools for modernization and scale. UP is establishing integrated textile parks (greenfield) under the Government of India’s Mega Integrated Textile Region & Apparel (PM MITRA) initiative. In order to draw in high-value, export-focused units, PM MITRA parks UP Industrial Growth offers plug-and-play infrastructure, shared amenities, smooth connection, and incentives.
In an integrated chain, these parks will house spinning, weaving, dyeing/finishing, clothing, and related services. The goal is to increase competitiveness, decrease turnaround times, and lessen logistical friction. Thus, PM MITRA parks UP promotes the expansion of the UP textile sector not just by increasing volume but also by enhancing quality and efficiency.
Clusters of UP Technical Textiles
Beyond conventional textiles, UP technological textile clusters hold the key to the future. Technical textiles, which are utilized in automobiles, industrial filters, protective gear, geotextiles, and medical textiles, require more advanced technology, research and development, and specialized inputs. They also generate better profit margins. By creating clusters that connect upstream and downstream businesses, UP Industrial Growth is encouraging units to get into or diversify into technological textiles divisions. Technical textile capabilities become particularly relevant for the production of uniforms, ballistic textiles, and specific protective gear against the backdrop of defense manufacturing growth.
3. Heritage & Innovation: Handloom, Powerloom & Silk
Handloom Powerloom UP in Lucknow and Bhadohi
The handloom powerloom UP’s twin forces The soul and texture of Uttar Pradesh’s textile heritage are embodied by Bhadohi and Lucknow. The powerloom and carpet weaving industries in Bhadohi are widely recognized around the world. In both local and international markets, Lucknow’s handloom heritage—known for its Chikankari designs—commands premium appeal. Modernizing without sacrificing artisan uniqueness is a difficult task.
The UP textiles policy 2022 offers incentives for the establishment of new powerlooms or handlooms in specific zones, including a 75% capital subsidy in some configurations.
Additionally welcomed are design studios, export houses, and marketing assistance.
Exchange of Silk in Varanasi
A crucial aspect of Varanasi’s textile character is silk hanging. However, adulteration concerns, middleman margins, and supply constraints plague silk value chains. A Silk Exchange Varanasi, a transparent marketplace for silk yarn, raw silk, and weaving contracts, is suggested as a solution to this problem. The region’s weaving ecology would be strengthened by this exchange, which would facilitate price discovery, traceability, and direct connections between producers and purchasers.
4. The Defence Pivot: Corridor, Nodes & Investments
Investment in the UP Defence Industrial Corridor
Although UP’s traditional strength has been its textile growth, the most recent drive has been toward defense, with investments in the UP Defence Industrial Corridor creating new industrial dynamics. Kanpur, Lucknow, Jhansi, Aligarh, Agra, and Chitrakoot are the six important nodes that make up the Uttar Pradesh Defence Industrial Corridor (UPDIC).
More than ₹33,896 crore worth of investment bids have been received, according to press reports.
Defense companies have been granted access to agricultural land, and a number of their units are currently in operation.
This level of investment is a blatant indication that UP wants to become a major center for defense manufacture in addition to textiles.
UP Nodes for Defense Manufacturing
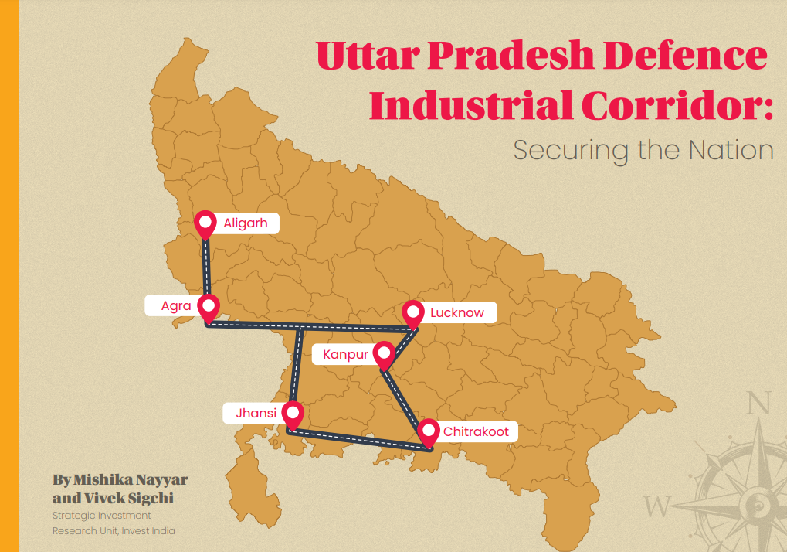
Each node is supported by incentives and infrastructure and focuses on specific defense technologies:
- Kanpur: Focus on manufacturing ammunition, safety gear, defense textiles, and ballistic materials.
- Lucknow: Excellent prospects for innovative materials, logistics support, and missile systems.
- Jhansi: Dedicated to the production of ordnance, ammunition, and propellants.
- Aligarh: precise parts, radar, small guns, and electronic warfare systems.
- Agra: Despite their current lesser scale, Agra and Chitrakoot serve as vital hubs for the production of components, support services, and spillover industries.
The defense manufacturing UP Industrial Growth nodes come together to form a dispersed yet connected system where supply chains, R&D, testing, and production all come together.
5. Synergies & High-Performance Textiles in Defence
Kanpur’s Ballistic Materials Production
The manufacture of ballistic materials in Kanpur is one of the most interesting nexus points between textile and defense. Bulletproof vests, helmets, and armour plates require high-performance fibers, composites, and ballistic protective materials, which are being developed by businesses like AR Polymers in the Kanpur node.
This production calls on knowledge of sophisticated textile and materials engineering fields such as fiber science, composite stacking, and heat and chemical resistance. The existence of this capacity at UP establishes UP as a leader in defense-grade textiles and supports the growth story of the UP textile industry as a whole.
UP Defense MSMEs
Small and medium-sized businesses are the foundation of any ecosystem centered around defense manufacture. To manufacture parts, subassemblies, textile inserts, filters, fasteners, etc., defense MSMEs UP Industrial Growth are being incorporated into supply chains. Many MSMEs with roots in textile value chains can diversify or pivot into defense suppliers, particularly in protective materials, specialist weaving, and finishing, thanks to the synergy with textile clusters. As a result, industry diffusion is accelerated and entrance barriers are reduced.
6. Policy & Strategic Anchors: “Make in India”, Exports & Self-Reliance
Growth in Made-in-India Defense Exports
India’s defense exports are expanding quickly. Indian defense exports reached USD ~2.63 billion in FY24, a ~32.5% increase from the year before.
The defense corridor in Uttar Pradesh is intended to make a substantial contribution to this course. The state supports the national initiative under “Make in India” to boost exports of defense systems and hardware by producing electronics, textiles, ammunition, and equipment in Uttar Pradesh.
Defence of Atmanirbhar Bharat UP
Self-reliance in defense production is promoted by UP’s corridor projects, incentives, and industrial alignment under Atmanirbhar Bharat Defence UP. Reducing reliance on imports, increasing domestic capability, and integrating technology into the state are the objectives. In Uttar Pradesh, the defense corridor is a concrete manifestation of Atmanirbhar Bharat.
FDI in India’s Defense Sector by 2025
FDI in India’s defense sector is encouraged through 2025 in order to increase technology, cash, and international connections. Significant foreign investment is allowed in the UP defense corridor under restricted procedures, facilitating co-production, advanced collaboration, and knowledge transfer. This makes it possible for international OEMs to locate offices in Uttar Pradesh or form advantageous partnerships with regional businesses.
7. Exports & Employment: Textile Export UP India & UP Apparel Industry Jobs
India’s Textile Export UP
Through its clusters (silk, carpets, handloom, and clothing), Uttar Pradesh contributes to the country’s textile exports. India’s textile exports are expected to develop significantly with better global connections, more integration through PM MITRA parks, and improved regulatory assistance. This is further supported by subsidies, freight reimbursement, and export incentives under the UP textiles strategy 2022.
In order to boost its export share, UP must also make investments in design, compliance (social standards, sustainability), and branding as the global market becomes more competitive.
Jobs in UP’s Apparel Sector
Manufacturing expansion inevitably results in the development of jobs. UP’s textile industry already provides employment in spinning, weaving, finishing, clothing, and related services for the UP Industrial Growth apparel industry. Thousands of new jobs are anticipated as a result of the recent wave of investments in PM MITRA parks UP, cluster expansions, and export focus. For instance, more than one lakh employment are expected to be created by the 95 Memorandums of Understanding inked under UP’s textile expansion strategy.
Beyond traditional weaving and clothing employment, technical positions, research and development, quality control, and highly skilled labor may become more in demand due to the growth of both the textile industry and defense.
8. Challenges, Risk & Strategic Moves
Obstacles and Bottlenecks
Infrastructure delays: Roads, utilities, electricity supplies, and purchasing land are still possible obstacles to travel, particularly in isolated or poorly developed regions.
Skill gaps: New abilities and training are required when switching away from conventional loom weaving to sophisticated textiles or defense manufacture.
Technological & R&D: Strong research, testing facilities, and innovation support are necessary for precise defense systems, ballistic material composites, and high-performance textiles.
Competitiveness and enabling environment: Other states or nations might provide cheaper prices; UP Industrial Growth needs to maintain its lead in terms of quality, efficiency, policy, and ease of doing businesses.
Sustainability and regulatory risk: Textile production may have an effect on the environment due to chemicals and waste water. Security, compliance, and quality risks are present in defense manufacturing.
Strategic Actions & Improvements
- Develop the synergy between textile and defense: Promote collaborations between textile corporations and defense technology companies, particularly in the areas of smart apparel, protective gear, and ballistic fabric.
- Concentration of parks and clusters: To maximize inputs and understanding spillovers, some parks or clusters can specialize, such as one for textile finishing, one for technical textiles, or one for protective textiles in defense.
- Upgrading skills and technology: Create training facilities and institutes specializing in defense electronics, composite materials, and technical textile technology. Join forces with the research labs at IIT and BHU.
- Enhance MSME infrastructure: To help MSMEs integrate into the supply chain, offer them subsidies, loans, marketing support, and incubation.
- Exporter readiness and brand building: Assist businesses with worldwide business-to-business relationships, trade missions, legal compliance (labor, sustainability), and accreditation (ISO, defense standards).
- R&D and innovation ecosystems: Establish test facilities, labs in strategic locations, and support startups in smart fabrics, additive manufacturing, and defense textiles.
- Balanced regional growth: Provide more subsidies in Poorvanchal or Bundelkhand to encourage inclusive growth; make sure underdeveloped areas receive incentives to lessen inequality.
Conclusion: Accelerating UP Industrial Growth
Uttar Pradesh is at a pivotal moment in its industrial history. The state is positioned for revolutionary transformation as a result of the transition from the rise of the UP textile industry, which was founded on craftsmanship, to a daring, diversified economic strategy that includes investments in the UP defense industrial corridor and defense textile efficiencies.
PM MITRA parks UP and UP technical textiles clusters bring scale and modernity; handloom powerloom UP Bhadohi / Lucknow and silk exchange Varanasi anchor tradition within contemporary supply chains; and the UP textiles policy 2022 offers the framework for encouraging the growth of traditional and technical textiles. On the defense side, Atmanirbhar Bharat defense UP, ballistic materials production Kanpur, defense MSMEs UP, defense manufacturing UP Industrial Growth nodes, and allowed FDI in the defense sector India 2025 map out a route to independence and export leadership.
Jobs in the UP apparel industry and textile exports from India, meanwhile, demonstrate the dual-engine model’s economic and social effects.
Although there are obstacles along the way, the policy, momentum, and industry goal are all evident. A strong representation of UP Industrial Growth, UP has the potential to emerge as a major worldwide center for the production of defense and advanced textiles with well-coordinated execution.